By Parul Jain and Olusola Omotoso
Broadly stated, financial literacy refers to the knowledge and skills necessary for making sound financial choices within a business context, which is deemed critical for business operation and growth. While definitions and measurements of financial literacy diverge considerably across different studies, such a measure should capture the degree to which an individual comprehends and utilizes various financial skills, including personal financial management, budgeting, investing, and understanding and managing debt. Improved financial literacy is integral for empowering entrepreneurs towards obtaining favorable financing, driving innovation, and ultimately achieving stronger business growth. This aspect is particularly important for micro-, small- and medium-sized enterprises (MSME) and more so for minority-owned businesses, since it is well documented that higher financial literacy is associated with better access to external funding which leads to improved business performance.[1]
New Jersey is recognized for its diverse population and thriving minority business sector. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration Office of Advocacy (SBAOA), as of 2022, there were 952,029 small businesses in New Jersey, comprising 99.6% of all businesses in the state, with minority-owned businesses representing 23% of the total. Small businesses in New Jersey employed 1.9 million people, accounting for 48.8% of the state’s workforce (SBAOA, 2023).[2] In addition, the distribution of small businesses across various industries highlights the diversity in New Jersey’s economy, with significant numbers in sectors such as professional/scientific/technical services, transportation/warehousing, real estate/construction, and rentals and leasing.
How is New Jersey faring on the financial literacy front? Our inputs for the Financial Literacy Index were obtained from the FINRA National Financial Capability Study (NFCS). It shows the overall financial knowledge (interest rates, inflation, diversification, etc.), categorizes financial education attainment (formal or informal training) along with an overall understanding of financial products (mortgages, bonds, etc.). A scaled score is obtained from the NFCS inputs, with 100 representing the highest financial literacy possible.
The state level comparison in the graphs below shows that the average financial literacy index across all U.S. states was 59.49 points out of 100 in 2021. New Jersey ranked 25th with a score of 59.65, which is slightly above the national average but considerably below the Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) suggested target score of 70 points. The OECD target was established to be consistent with definitions of minimum competency in financial knowledge and concepts. More troublesome is the fact that the financial literacy index for New Jersey fell after 2015, indicating a declining understanding of key financial concepts over these years. Such a decline is likely due to economic shifts, policy changes, financial education efforts, and changing demographics. The 2018 and 2021 declines also suggest reduced focus on financial literacy along with potential COVID-related economic hardships. On balance, the data clearly highlights the dire need for continued and targeted financial literacy programs.
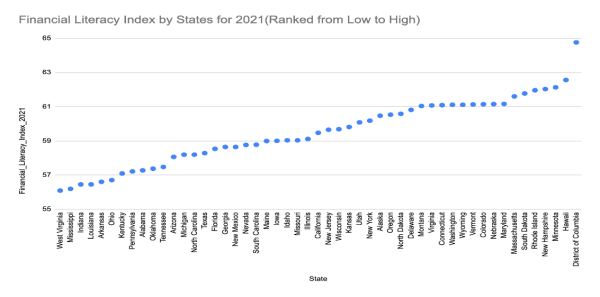
Data Source: NFCS, Own computations
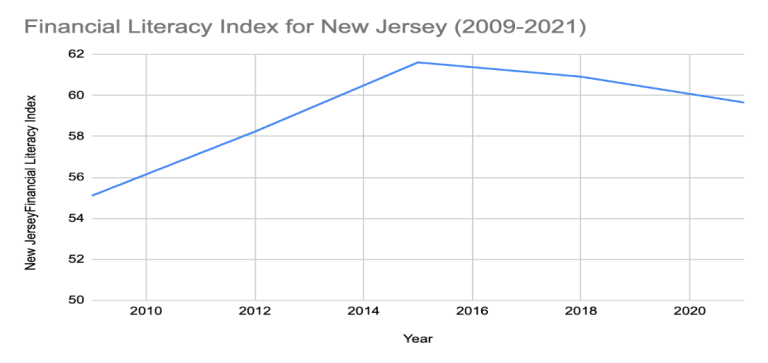
Data Source: NFCS, Own computations
Parul Jain is a Finance and Economics Associate Professor at the Rutgers Business School and Olusola Omotoso is a graduate student pursuing a Doctor of Business Administration degree.
References:
[1] The Small Business Administration (SBA) defines MSMEs based on the number of employees and annual revenue of the business. Micro enterprises employ fewer than ten people and gross less than $1 million annually. Small enterprises have fewer than 500 employees with less than $100 million in annual revenue. Medium enterprises clear less than $750 million per year and have a staff of less than 1500.
[2] For the entire U.S., there were 33.3 million small businesses, comprising 99.9% of all businesses, with minority-owned businesses representing 20.4% of the total. Small businesses in the U.S. employed 61.7 million people, accounting for 46.4% of the workforce (SBAOA, 2023).
